Node.js MongoDB
Node.js MongoDB
Hi guys.. you will try it !........
* To create a database in MongoDB, start by creating a MongoClient object, then specify a connection URL with the
correct ip address and the name of the database you want to create.
* MongoDB will create the database if it does not exist, and make a connection to it.
2.Creating a Table
* To create a table in MongoDB, use the
3.Insert Into Table
* To insert a record into a table in MongoDB, we use the
* The first parameter of the
* It also takes a callback function where you can work with any errors, or the result of the insertion:
* The first argument of the
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myquery = { name: "Mayoori" };
var newvalues = {$ins:{Assignment_Marks:6} };
db.collection("student_marks").update(myquery, newvalues, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(res.result.nModified + " record updated");
db.close();
});
});
* The
* The first parameter of the
* The
* The first parameter of the
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
* By default, the
* The first parameter of the
* The second parameter is an object defining the new values of the document. By default, all fields in the document gets updated, (except the
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/Uki_Student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myquery = { name: "Thadsha" };
var newvalues = {$set:{Assignment1_Marks:75} };
db.collection("student_marks").update(myquery, newvalues, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(res.result.nModified + " record updated");
db.close();
});
});
* The first parameter of the
* The
Hi guys.. you will try it !........
--Today we learn how to connecting nodejs_mongodb--
* MongoDB will create the database if it does not exist, and make a connection to it.
Create a Database called Uki_student
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Database created!");
db.close();
});
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Database created!");
db.close();
});
* To create a table in MongoDB, use the
createCollection() method:
Create a collection called studentmarks
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
db.createCollection("student_marks", function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Table created!");
db.close();
});
});
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
db.createCollection("student_marks", function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Table created!");
db.close();
});
});
* To insert a record into a table in MongoDB, we use the
insertOne() method.* The first parameter of the
insertOne() method is an object containing the
name(s) and value(s) of each field in the record you want to insert.* It also takes a callback function where you can work with any errors, or the result of the insertion:
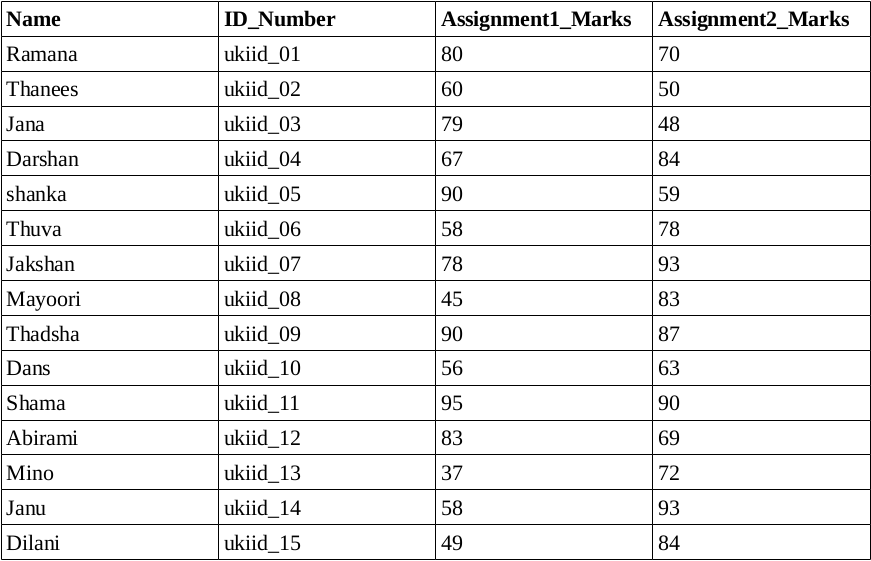
Create the documents listed in above table
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myobj = [
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myobj = [
{Name: "Ramana",ID_Number:ukiid_01,Assignment1_Marks:80,Assignment2_Marks:70 },
{Name: "Thanees",ID_Number:ukiid_02,Assignment1_Marks:60,Assignment2_Marks:50 },
{Name: "Thanees",ID_Number:ukiid_02,Assignment1_Marks:60,Assignment2_Marks:50 },
{Name: "Jana",ID_Number:ukiid_03,Assignment1_Marks:79,Assignment2_Marks:48 },
{Name: "Darshan",ID_Number:ukiid_04,Assignment1_Marks:67,Assignment2_Marks:84},
{Name: "Shanka",ID_Number:ukiid_05,Assignment1_Marks:90,Assignment2_Marks:59 },
{Name: "Thuva",ID_Number:ukiid_06,Assignment1_Marks:58,Assignment2_Marks:78 },
{Name: "Jakshan",ID_Number:ukiid_07,Assignment1_Marks:78,Assignment2_Marks:93},
{Name: "Mayoori",ID_Number:ukiid_08,Assignment1_Marks:45,Assignment2_Marks:83},
{Name: "Thadsha",ID_Number:ukiid_09,Assignment1_Marks:90,Assignment2_Marks:87},
{Name: "Dans",ID_Number:ukiid_10,Assignment1_Marks:56,Assignment2_Marks:63},
{Name: "Shama",ID_Number:ukiid_11,Assignment1_Marks:95,Assignment2_Marks:90},{Name: "Abiramy",ID_Number:ukiid_12,Assignment1_Marks:83,Assignment2_Marks:69 },
{Name: "Mino",ID_Number:ukiid_13,Assignment1_Marks:37,Assignment2_Marks:72 },
{Name: "Janu",ID_Number:ukiid_14,Assignment1_Marks:58,Assignment2_Marks:93 },
{Name: "Dilani",ID_Number:ukiid_15,Assignment1_Marks:49,Assignment2_Marks:84},
];
db.collection("student_marks").insert(myobj, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Number of records inserted: " + res.insertedCount);
db.close();
});
});
db.collection("student_marks").insert(myobj, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Number of records inserted: " + res.insertedCount);
db.close();
});
});
4.Node.js MongoDB Query
* When selecting records from a table, you can filter the result by using a query object.* The first argument of the
find() method
is a query object, and is used to limit the search.
Increase the maths marks of Mayoori by 10Assignment1_Marks
var url = "mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myquery = { name: "Mayoori" };
var newvalues = {$ins:{Assignment_Marks:6} };
db.collection("student_marks").update(myquery, newvalues, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(res.result.nModified + " record updated");
db.close();
});
});
5.Node.js MongoDB Select From
-Select One-
* To select data from a table in MongoDB, we can use thefindOne() method.* The
findOne() method returns the first
occurrence in the selection.* The first parameter of the
findOne() method
is a query object. In this example we use an empty query object, which selects
all records in a table (but returns only the first record).-Select All-
* To select data from a table in MongoDB, we can also use thefind() method.* The
find() method returns all
occurrences in the selection.* The first parameter of the
find() method
is a query object. In this example we use an empty query object, which selects
all records in a table.List the names of students who got more than 50 marks in Assignment1_Marks.
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var options={Assignment1_Marks:1,_id:0}
db.collection("student_marks").find({Assignment1_Marks:{$gt:50}},options).toArray(function(err, result) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(result);
db.close();
});
});
6.Node.js MongoDB Update
* You can update records, or documents as it is called in MongoDB, by using theupdate() method.* By default, the
update() method only updates
one document.* The first parameter of the
update() method
is a query object defining which document to update.* The second parameter is an object defining the new values of the document. By default, all fields in the document gets updated, (except the
_id field)
so remember to set the value of every field, otherwise the value will be left
empty.
Update Assignment1_Marks=75 to Thadsha
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/Uki_Student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myquery = { name: "Thadsha" };
var newvalues = {$set:{Assignment1_Marks:75} };
db.collection("student_marks").update(myquery, newvalues, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(res.result.nModified + " record updated");
db.close();
});
});
7.Node.js MongoDB Remove
* You can delete records, or documents as it is called in MongoDB, by using theremove() method.* The first parameter of the
remove() method
is a query object defining which documents to delete.
Remove Assignment2_Marks column/field for Ramana
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myquery = {name: "Ramana" }
var newvalues = {$unset: {Assignment2_Marks: ""} };
db.collection("student_marks").update(myquery, newvalues, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(res.result.nModified + " record updated");
db.close();
});
});
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_student";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
var myquery = {name: "Ramana" }
var newvalues = {$unset: {Assignment2_Marks: ""} };
db.collection("student_marks").update(myquery, newvalues, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(res.result.nModified + " record updated");
db.close();
});
});
8.Node.js MongoDB Drop
* You can delete a table, or collection as it is called in MongoDB, by using thedrop() method.* The
drop() method takes a callback function
containing the error object and the result parameter which returns true if the collection was dropped successfully,
otherwise it returns false.
Delete the "student_marks" table:
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_students";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
db.collection("student_marks").drop(function(err, delOK) {
if (err) throw err;
if (delOK) console.log("Table deleted");
db.close();
});
});
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/Uki_students";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
db.collection("student_marks").drop(function(err, delOK) {
if (err) throw err;
if (delOK) console.log("Table deleted");
db.close();
});
});



Comments